Aspergillus
CASE 1
• A 68 year old man comes in after an episode of sudden coughing of bright red blood in large quantities. The coughing and bleeding stops after 20 minutes.
• The patient was successfully treated for cavity tuberculosis 10 years earlier.
• An x-ray of his chest shows a discrete round density in his right upper lobe (blue arrows) that appears to be resting within a larger cavity.
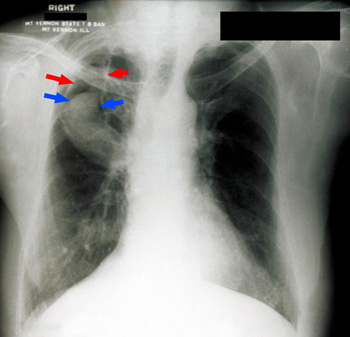
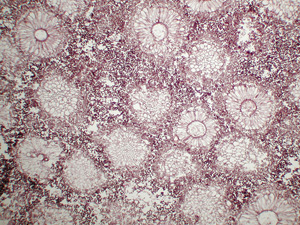
• An operation is performed to remove the right upper lobe. The histolopathology confirms that radiographic impression of a fungal ball within a cavity with a recent eroded blood vessel adjacent to the fungus ball. The ball itself consists of a mass of acute-angle branching hyphae (mostly in cross-section) and conidia typical of Aspergillus (looking like flower heads in cross-section).
Questions:
1. How did the patient acquire Aspergillus in his lung?
2. What was the form of the fungus that he inhaled?
3. Why would not expect antifungals to be of much benefit in this patient?
4. Why was it deemed necessary to operate on this patient to remove the fungus ball?
5. Is this man immunocompromised?
CASE 2
• An 18 month old girl present with fever and respiratory distress.
• A complete blood count shows a hemoglobin of 8.3gm/dL and a white blood cell count of 2,200/mm3 with 97% blasts, 1 neutrophil, 1 eosinophils, and one basophil. The platelet count is 25,000/mm3.
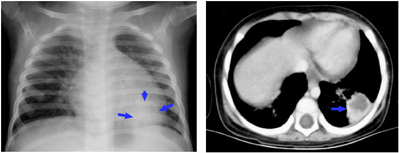
• An xray of the chest shows a nodular lesion in the left lower lobe behind the heart shadow (below, left, blue arrows). A chest CT scan is performed, and a section of the scan at the level of the mass is shown (below, right). On the CT scan, the mass appears to be undergoing central necrosis.
• A tracheal aspirate grows Aspergillus fumigatus. The patient is started on voriconazole therapy.
Questions:
1. What is the nature of this patient's infection?
2. Does the isolation of Aspergillus in the sputum also denote the presence of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis? Why is it the diagnosis in this case?
3. What is voriconazole, and why is it used in this situation instead of fluconazole or amphotericin?
4. What is the likely that this child will survive?
5. What other types of patients are at risk of getting invasive pulmonary aspergillosis?